Business-to-business (B2B) companies today can choose from a growing number of sophisticated options to make and receive payments. Driven by their need for greater speed, fewer errors, lower costs, and better security, companies are adopting new technologies to pay — and be paid by — partners, contractors, product distributors, and suppliers.
The demand for better B2B payment systems is a boon for payment service providers. Allied Market Research valued the global B2B payments market at $870.42 billion in 2020 and projected that it would reach $1.91 trillion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6%.¹
The key differentiator among payment service providers today is their ability to provide an integrated payment processing solution that will address the needs of B2B companies. This can make all the difference when it comes to lowering costs, boosting cash flow, speeding up funding times, and improving business efficiency. In this white paper, we will give an in-depth overview of the B2B payments infrastructure, discuss how B2B payment technology is evolving, and explore what B2B businesses and Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) should look for when seeking payment processing technology to facilitate payments.

What are B2B Payments?

B2B payments are accounts payable and accounts receivable transactions between businesses. Unlike business-to-consumer (B2C) payments that are paid at the point of sale, B2B payments are typically made after the goods or services are delivered. The usual process is as follows: the customer places an order, the provider fulfills the order and sends an invoice to the purchaser, the purchaser checks the invoice against the terms of the purchase order and pays the balance, and the provider receives the payment and updates their records. Some of these steps are done manually, and the entire process usually involves several teams of employees. In sizable companies with active accounts payable and receivable — especially those that rely on physical invoices and checks — this can be time-consuming, costly, and prone to error and fraud.
Characteristics and Costs of B2B Payment Types
Businesses make and receive payments using a wide range of payment methods, and each has its own costs, advantages, and risk profiles. Here we will briefly review their pros and cons.
Checks
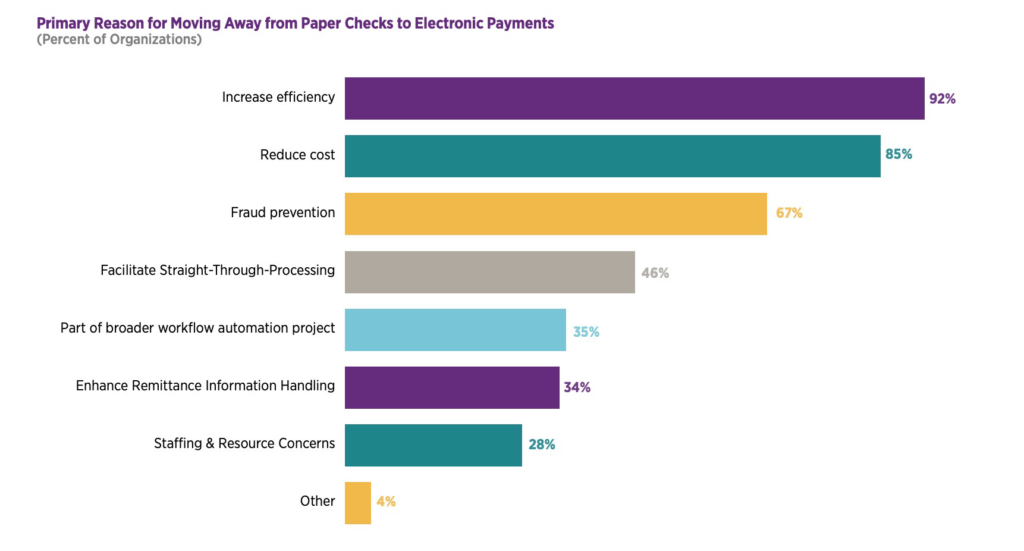
The use of checks for B2B payments remains widespread, despite their drawbacks. In 2018, checks accounted for 32.4% and 34.4% of receivables and payables transactions, respectively. However, check use is declining for a variety of reasons (see graph on page 5). The Association for Finance Professional (AFP)’s 2019 survey showed that 42% of U.S. B2B payments were made by check, down sharply from the 81% reported in 2004.
- Risk Profile
Since checks rely on the postal service and, upon arrival, have to be handled by multiple employees, they are the slowest form of payment and the most susceptible to error and fraud. According to the AFP’s 2022 Payments Fraud and Control Survey, checks were the payment method most impacted by fraud activity, accounting for 66% of fraudulent cases. - Cost Profile
Checks are not an economical way of making payments. Although technology has reduced some of the costs, wages for employees who handle checks have offset these savings. The AFP’s 2022 Payments Cost Benchmarking Survey showed that, on average, it cost between $2.01 and $4.00 to issue a check in 2021 — the same as it cost in 2015. The cost to receive a check is lower — $1.01 to $2.00 – because the receiver does not have to bear as many costs, such as printing and postage.
Graph 1: Primary Reason for Moving Away from Paper Checks to Electronic Payments
Automated Clearing House (ACH)
ACH payments are among the most commonly used by B2B organizations. The AFP found that 87% of its 2022 survey respondents accept ACH credit transactions and 73% accept ACH debit transactions for incoming payments, while 78% use one or the other to make outgoing payments.
The introduction of real-time payment technology is driving the growth of ACH. In 2017, The Clearing House launched RTP (Real-Time Payments) so that consumers and businesses could conveniently send ACH payments directly from their accounts at federally insured depository institutions 24/7, and receive and access funds sent to them over the RTP network immediately. In 2023, the Fed plans to launch another real-time payments system called FedNow.
- Risk Profile
ACH transfers are one of the most popular B2B payment options. They are secure, and transactions can be arranged to clear on the same day. - Cost Profile
The 2022 AFP Payments Cost Benchmarking showed that ACH transfers cost, on average, $0.26 to $0.50 per transaction, which is unchanged from 2015.
Wire Transfers
Wire transfers are also electronic fund transfers from one bank account to another, but, unlike ACH transfers, a wire system such as Fedwire or The Clearing House Interbank Payments System (CHIPS) provides immediate and final settlement. This payment method is popular in the capital markets, real estate, and financial services sectors due to its high level of security.
- Risk Profile
Wire transfers are irrevocable and confirmed upon receipt. Wire transfers are therefore used for large, lower volume, time-sensitive transactions. - Cost Profile
The average cost of a wire transfer, including more expensive international wires, ranges between $10.01 and $15.00, with some costing as much as $50, according to the AFP’s 2022 Payments Cost Benchmarking survey. The median cost of receiving a wire is about $10.00.
Credit Cards
While in the past credit cards were used primarily for B2C payments, in recent years they have grown in popularity in the B2B space. In 2021, two-thirds of the companies surveyed by the AFP used credit cards for accounts receivables.
Credit cards are often used for smaller transactions, in part because of the fees they impose. The median average incoming credit card transaction from the AFP’s 2022 Payments Cost Benchmarking survey ranged between $300 and $499. Only 9% of the companies surveyed said that the average size of their credit card transactions exceeded $15,000. The median size has increased since 2015, when it ranged between $200 and $299. That could be due to companies’ desire to minimize manual transactions during the COVID-19 pandemic, along with improvements in card transaction integration with ERP, accounting, and other back-office systems.
- Risk Profile
Credit card transactions are subject to fraud and chargebacks, which can cost businesses a great deal of money. Card transactions also sometimes fail when the card is inactive or expired - Cost Profile
As with B2C card transactions, the 3-4% that card issuers charge on every transaction can add up fast. However, B2B businesses often qualify for special cost savings that are not available to B2C vendors and which make card transactions more economical.
Challenges of Today’s B2B Payments
Now that we’ve discussed the payment infrastructure and technologies used in the B2B sector, let’s take a look at some of the overarching challenges posed by B2B payments. Later on, we will discuss how the below pain points reinforce the need for B2B payment integrations that streamline access to electronic payment methods.
Four Common Pain Points:
- Manual Reconciliations
When payment processing software and the business’s ERP or accounting software aren’t integrated, then account reconciliations must be performed manually. This tedious process, in which employees input transaction data into the company’s software, is time-consuming and prone to errors. - Long Payment Cycles
Long payment cycles, such as net 90 days, commonly delay revenue funding. This can have a knock-on effect throughout the enterprise, especially for seasonal companies like agricultural businesses, which may have to tap short-term credit lines to meet expenses until their receivables arrive. - Missed or Late Payments
Missed payments due to data input issues, declined cards, and so on, are common — requiring companies to chase after customers for payment details. This is time-consuming, and if the missed payment was due to a logistical problem rather than a failure to pay, it can impact client relationships. - Processing Costs
As noted above, high credit card processing costs can dent revenues. This is also the case with checks, which incur added costs such as wages needed for the employees who process check payments.
Addressing the Challenges — And Trends — of B2B Payment Tech
B2B is on track to experience a technological revolution that will solve the problems listed above, among many others. In fact, a recent survey revealed that 86% of executives consider it at least moderately important to improve their current digital payment capabilities. This process has by and large already occurred for B2C payments, with 82% of Americans having reported using some form of digital payment in 2021.
While progress is lagging in the B2B industry, it is indeed occurring. Here’s a look at some of the latest trends and innovations for B2B payments:
The Shift Toward Electronic Payments
Nearly three-quarters of those surveyed in AFP’s 2022 Payments Cost Benchmarking Survey reported that they are moving from checks to electronic payments “to increase efficiency, save money, and reduce costs.” The number of firms that need to make this transition remains high, however — according to the AFP’s survey, companies made 42% of their payments by check in 2021, and 92% accepted checks for incoming transactions. Other drivers of the transition toward electronic payments include:
Real-Time Payments
According to Mastercard’s The B2B Payments Tipping Point survey from 2018, RTP has several important advantages, including:
- Efficient e-invoicing and billing
- Improved liquidity management
- Optimized working capital management
Mastercard’s survey found that real-time payment adoption is driven mainly by the need to improve the efficiency of payment systems (83%), respond to technological innovation (69%), and reduce systemic risks (63%).
E-Commerce
Investing in e-commerce capabilities is key to staying competitive. American Express’s B2B Payment Trends To Watch In 2021 survey found that 42% of small – and medium-sized B2B businesses experienced an increase in online transactions in Q2 and Q3 of 2020, and businesses implementing e-commerce expect to see five times faster revenue growth. Forrester forecasts that B2B e-commerce in the U.S. will reach $1.8 trillion and account for 17% of all B2B sales by 2023.
Virtual Card Spending
Virtual cards are essentially one-time-use credit card numbers that link to an existing credit card. According to American Express’s B2B Payment Trends to Watch in 2021 report, virtual card spend is forecasted to grow from $213.8 billion in 2021 to $414.2 billion in 2024. This is likely due to the robust security that virtual cards provide, especially at a time when credit card fraud is on the rise — between 2019 and 2020, reports of credit card fraud for new accounts increased by an astounding 48%.

The Importance of Integrated Payments in the B2B Industry
In order to cater to the latest B2B payment trends, businesses in the industry as well as the ISVs who serve them will benefit greatly from integrating advanced payment processing solutions within B2B software. These solutions can make all the difference when it comes to improving business efficiency by lowering costs, boosting cash flow, and speeding up funding times. Here are some specific benefits of payment integrations:
- Recurring Payments
Automated recurring payments help businesses reduce the number of declined transactions while improving the customer bill paying experience. With recurring payments, there is no need for the customer to provide their payment details every time. Plus, with the help of account updater tools, expired or inactive cards are updated automatically so that the business doesn’t have to chase down the customer for new card information. - Support for a Large Range of Payment Methods
Integrating an advanced payment processing solution gives businesses the ability to accept a wide variety of today’s popular payment methods. This is increasingly important as more and more businesses prefer to make payments not just with checks or ACH but also with corporate credit cards and digital wallets. - Easier Account Reconciliations
When a payment gateway is integrated with the business’s software, transaction data is input automatically, eliminating the need for manual entry and improving data accuracy. - Lower Credit Card Processing Rates
As mentioned earlier, credit card processing rates are often a deterrent for B2B providers. However, the right payment technology provider will have the expertise to keep rates as low as possible. For example, B2B credit card processing can often be greatly reduced with the help of Level 2 and Level 3 processing, which are processing methods in which more card data is submitted to the processing bank.
Upgrade Your B2B Payments With Sola
Sola is a leading payment technology provider for the B2B sector. We equip ISVs and their clients with advanced payment processing tools that improve efficiency and grow revenue for B2B clients. Here’s a look at some of our solutions:
Software Integrations
The Sola gateway can be easily integrated with a wide range of ERP, POS, and accounting software. Choose from our plugins to get up and running fast, or build a custom integration with our powerful SDK and API.
Sola Merchant Portal
The Sola Merchant Portal is a web-based virtual terminal solution that gives merchants all the tools they need to manage their payment activity right from their computer. Users can process one-time and recurring payments, view sales data, generate reports, securely store customer payment details, and much more. Plus, the Sola Merchant Portal is fully synced with the Sola Mobile App so you can access data and take payments wherever you are.
Recurring Payments
Available through the Sola Merchant Portal or a custom integration, Solas recurring payment solution makes it easy for businesses to set up precise schedules with preferred payment amounts, frequencies, intervals, and more. Plus, businesses can rest assured that inactive or expired cards won’t cause them to lose out on sales — Sola’s Account Updater tool automatically scans payment information stored on file to detect any that have expired or are inactive. Then, it reaches out to the card brand to get the new card information and updates the system accordingly.
PaymentSITE
Sola PaymentSITE is an online form that can be embedded into an existing webpage or used as a standalone form to collect payments. It is fully customizable and can be pre-filled with transaction details. For easy email invoicing, merchants can use our Sola Merchant Portal to send out PaymentSITE invoices with just a few clicks.
Hardware Integrations
Sola can be integrated with a wide range of card readers and terminals for in-person payment acceptance. Businesses can choose from our extensive lineup of wireless and unattended devices that feature NFC, magstripe, and EMV readers.
Interchange Qualification Monitoring (IQM)
IQM is our interchange optimization tool that ensures that each and every transaction is processed at the lowest rate possible. Sola IQM technology automatically supplements transaction data with additional data points to secure the lowest rates. This includes Level 2 and Level 3 processing, which provides more transaction data such as PO numbers and tax amounts to qualify for lower rates.
Split Capture
Sola Split Capture is a great tool for wholesalers who send out orders in multiple shipments. It allows businesses to authorize the total or estimated total amount at the time of sale, and then capture multiple portions of the order as each shipment goes out. Users of this tool benefit from greater control over their payment processing flow and more organized records in which payments adequately reflect shipments.
Support For a Range of Payment Types And Currencies
Businesses today want the flexibility to pay with their payment method of choice. Fortunately, Sola supports a wide range of payment methods — including ACH, credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, cryptocurrencies, and more. Additionally, we support many international currencies including Euros, British Pounds, and Canadian Dollars.
Start Reaping the Benefits of Powerful Payment Technology
The advantages of having a best-in-class, integrated B2B system are increasingly important as businesses embrace new technologies that speed up the payment flow, reduce risk, and cater to the latest trends. Integrated payment technology is paving the way for the digitization of payment technology, and today’s ISVs will benefit greatly from implementing integrated payment solutions within B2B software. To learn more about how payment technology can supercharge B2B business operations and revenue, contact us today.